Need help? We're here to assist you!
Thank You for Enquiry, we will contact you soon!
Close
The Class 7 is an important year in a student’s life and Science is one of the subjects that require dedication, hard work, and practice. It’s a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your Class 7 journey even easier. It’s essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete NCERT Class 7 Science Book syllabus.

Exercise Questions
1. Why do organisms take food?
Solution:
All organisms require energy for their life processes. Plants prepare their food and acquire nutrients from abiotic components like soil, air, water and sunlight. On the other hand, animals need to get food from either plants or other animals to obtain nutrients; hence, animals need to take food to acquire nutrients and energy.
2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprophyte.
Solution:
| Saprophytes | Parasites |
| Acquire nutrients from dead and decaying matter. | Parasites live on or in a host and get their food at the expense of their host. |
| Example: Fungi | Example: Roundworm |
3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Solution:
Take two potted plants of the same kind. Keep one in the dark for 72 hours and the other in the sunlight. Perform the iodine test with the leaves of both plants as given below. Now, leave the pot, which was earlier kept in the dark, undisturbed for 3–4 days and perform the iodine test again on its leaves.
Iodine test:
Put iodine solution on the leaf.
Observation:
Blue-black colour will be observed on the leaves of the plant kept in sunlight, which indicates the presence of starch.
Blue-black colour will not be observed on the leaves of plants kept in the darkroom. This indicates the absence of starch.
4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Solution:
Green plants use a process called photosynthesis to prepare their food. The process is as follows
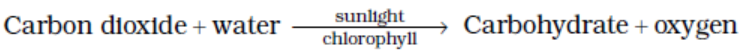
5. Show with the help of a sketch that plants are the ultimate source of food.
Solution:
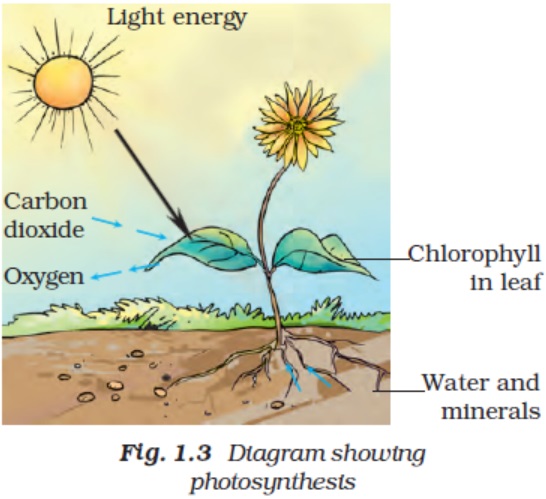
6. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Green plants are called _________________ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as _________________.
(c) In photosynthesis, solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called ___________.
(d) During photosynthesis, plants take in ______________________ and release __________________ gas.
Solution:
(a) Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesise their food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as starch .
(c) In photosynthesis, solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called chlorophyll.
(d) During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen gas.
7. Name the following.
i) A parasitic plant with a yellow, slender and branched stem.
ii) A plant that is partially autotrophic.
iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Solution:
i) Cuscuta
ii) Pitcher plant
iii) Stomata
8. Tick the correct answer.
(a) Cuscuta is an example of:
(i) autotroph
(ii) parasite
(iii) saprotroph
(iv) host
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) China rose
(iii) pitcher plant
(iv) rose
Solution:
(a) (ii) Parasite
(b) (iii) pitcher plant
9. Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| Chlorophyll | Rhizobium |
| Nitrogen | Heterotrophs |
| Cuscuta | Pitcher plant |
| Animals | Leaf |
| Insects | Parasite |
Solution:
| Column-I | Column-II |
| Chlorophyll | Leaf |
| Nitrogen | Rhizobium |
| Cuscuta | Parasite |
| Animals | Heterotrophs |
| Insects | Pitcher plant |
10. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Solution:
11. Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair (ii) Stomata (iii) Leaf veins (iv) Petals
Solution:
The answer is (ii) Stomata
12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots (ii) stem (iii) flowers (iv) leaves
Solution:
The answer is (iv) leaves
13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Solution:
Fruits and vegetable crops are grown in large greenhouses because it protects crops from external climatic conditions and provides suitable temperature for the growth of crops.
Advantages to farmers while growing fruits and vegetable crops inside greenhouses are
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 is colourful as it introduces you to the world of plants around you. The curriculum has a variety of projects that will make students enjoy the learning process. The curriculum introduces you to new terminology and concepts, which will make students look forward to studying this Chapter.
In Class 7 Nutrition in Plants Chapter, students will be introduced to many new concepts related to plants and how they get nutrition for themselves; they will also get to know about photosynthesis-process of preparation of food in plants, chlorophyll, and stomata. Various other modes of nutrition in plants, like insectivorous plants. This chapter will teach about the basics of plant nutrients and how plants make their food, but reading this chapter carefully will further help the students to understand the concepts of botany in higher standards. Therefore, it is highly recommended to prepare notes so that students can go through the while revising the Chapter for the exams.
Apart from this, by referring to these , students will also get to know about how nutrients are replenished in the soil, as we all know that nitrogen content is very much high in the air, but plants cannot take nitrogen through the air, and they need nitrogen in a soluble form. The bacterium called Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and can convert it to a usable form.